How to Provide Effective First Aid to an Open Wound

This week is Wound Awareness Week, a time to get people talking about the rising issue of wounds. In addition, Wound Awareness Week is to reach out to all, to help us spread awareness of what wounds are, who’s at risk, and what someone should do if they have a wound that won’t heal. Learn how to successfully provide emergency First Aid for a casualty suffering wounds or bleeding: Bitesize Wounds and Bleeding eLearning.
What exactly is an open wound?
An open wound is an injury involving an external or internal break in body tissue, usually involving the skin. Nearly everyone will experience an open wound at some point in their life. Most open wounds are minor and can be treated at home. However, in certain situations (such as one involving a major wound), immediate medical attention may be necessary. Read How to Provide First Aid to a Major Wound.
Falls, accidents with sharp objects, and car accidents are the most common causes of open wounds. In the case of a serious accident, you should seek immediate medical care. This is especially true if there’s a lot of bleeding or if bleeding lasts for longer than 20 minutes.

Understanding the different types of open wounds
When talking about wounds, there are four types of open wounds that need to be considered:
Abrasion
A type of open wound that’s caused by the skin rubbing against a rough surface, also known as a scrape or a graze. Abrasions are very common injuries and are most likely to occur on the elbows, knees, shins and upper extremities.
Laceration
A deep cut or tearing of your skin. Accidents with knives, tools, and machinery are frequent causes of lacerations. In the case of deep lacerations, bleeding can be rapid and extensive.
Puncture
A deep wound that occurs due to something sharp and pointed, such as a nail. The opening on the skin is small, and the puncture wound may not bleed much.
Avulsion
An avulsion is a partial or complete tearing away of skin and the tissue beneath. Avulsions usually occur during violent accidents, such as body-crushing accidents, explosions, and gunshots. They bleed heavily and rapidly.
It’s important to note that First Aid treatment differs depending on the type of wound.

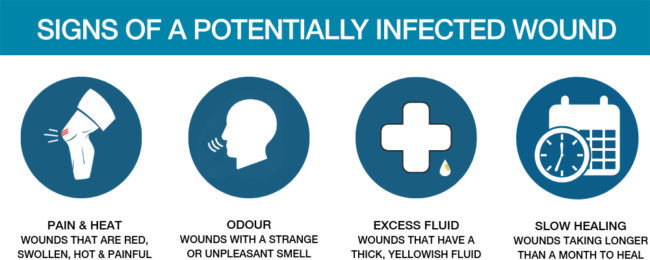
What are the warning signs of a potentially infected wound?
Seek immediate medical attention if you or someone in your family has any of these signs:
How to provide effective First Aid to Open Wounds?
Wounds can happen in a moment. Whether experiencing a major or minor wound, the following First Aid methods that can be applied to treat an open wound.
Minor Open Wounds
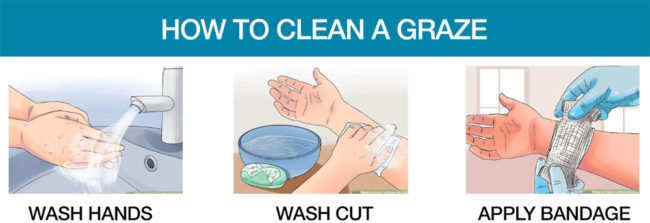
Grazes
- Wash hands to rid of any bacteria
- Wash graze with warm water and gentle soap using a gauze
- Put on a dressing to cover it once it’s cleaned; this can be either a band-aid or bandage, depending on the severity of the graze
Cuts
- Wash hands to rid of any bacteria
- Apply pressure to the cut
- Wash cut with warm water and gentle soap using a gauze
- Apply bandage to the cut
- If the cut continues to bleed, seek medical advice.

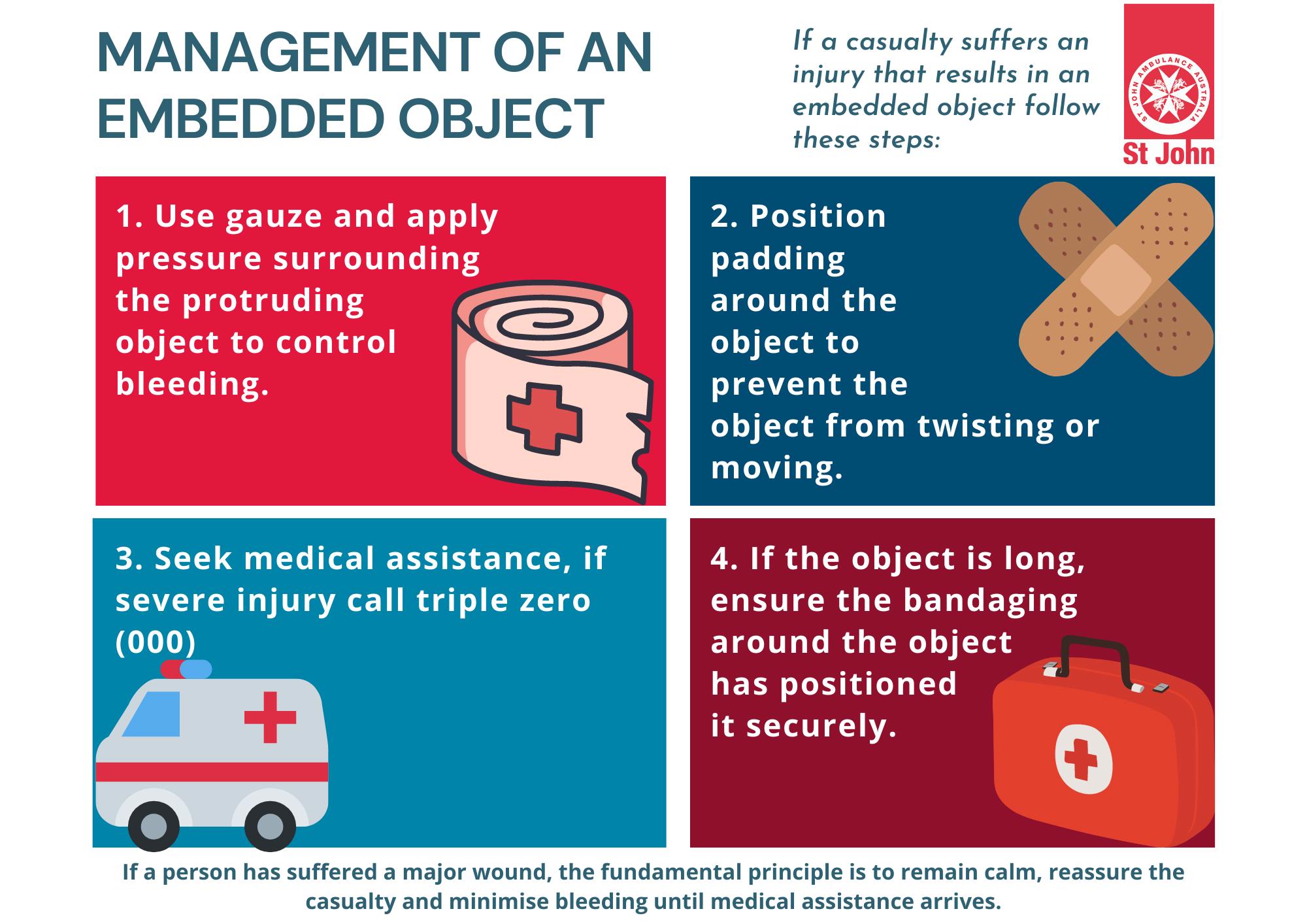
Embedded Object
- Apply pressure to the surrounding area of the protruding object to control bleeding
- Position padding around the object to prevent the object from twisting or moving, bandage over and around the padding to secure the foreign object
- If the object is quite long, ensure the bandaging around the object has positioned it securely
- Seek medical assistance, if severe injury or if you’re unable to safely move the casualty; call triple zero (000)
DO NOTs when providing First Aid for Embedded Objects
- DO NOT remove the embedded object as it may be preventing significant blood loss. The removal of the object could also cause major structural and nerve damage. It must always be completed by a professional
- DO NOT put any pressure on the object
- DO NOT cut the end of the object unless it’s completely unmanageable and causes you or medical professionals difficulty in moving the casualty
Puncture Wounds
- Remove any clothing covering the wound
- Keep the wound as clean as possible - if possible, do not use dirty clothing or materials
- If the wound is not bleeding, clean around it
- If the wound is bleeding, apply gauze around the wound and apply pressure to control bleeding
- DO NOT try to remove any foreign materials found in the wound
- Check if there is an exit wound on the opposite side of the opening
- Apply a sterile dressing
- Ensure casualty is seated in a comfortable position
- Seek medical assistance; call triple zero (000) if blood loss is severe
It’s important to be mindful that open wounds can become infected from the bacterial colonies present on the skin, so when treating a wound, it’s vital to practice proper sanitation to prevent any further infection.

INFECTION CONTROL ELEARNING
This convenient online course provides you with the knowledge to successfully provide first aid safely when there is a risk of infection to yourself and the casualty.

PROVIDE FIRST AID
Suitable for both people in workplaces and members of the public who would like a comprehensive first aid course.

DO YOU HAVE THE RIGHT FIRST AID KIT FOR YOUR HOME, SCHOOL OR WORKPLACE?
St John has a range of First Aid products to suit any situation.
