Lifesaving Tips for Head Injury First Aid Treatment

When it comes to first aid, head injuries are one of the most serious and challenging concerns to treat. Unless you see clearly visible bleeding or open wounds to the head, the brain may have sustained significant life threatening injuries. These hidden injuries can be the most concerning, as they usually don’t appear as serious as they truly are.
The possibility a head injury could result in permanent disability or impairment is real. Long term impacts can be life-altering and debilitating, such as chronic pain, paralysis, visual disturbances, poor memory and concentration, difficulty communicating and even changes in personality. Over 700,000 Australians have a brain injury that limits their daily activities and ability to participate, so swift first aid management of a head injury to prevent further damage is vital.
As it is difficult for a First Aider to make an accurate assessment of the severity of a head injury, you should always act with caution. Don’t disregard any head injury, even if the casualty appears as normal there is a possibility that complications could develop later. Make sure the casualty seeks medical aid and monitor them closely in the minutes, hours, days and even weeks following.
A blow to the head can cause bleeding within the brain, and often the blood can’t drain from within the closed space of the skull. This will put pressure on the brain, which is life-threatening.
As a rough guide the more forceful the impact was, the stronger the likelihood of a severe injury. This is particularly relevant if the casualty lost consciousness temporarily.
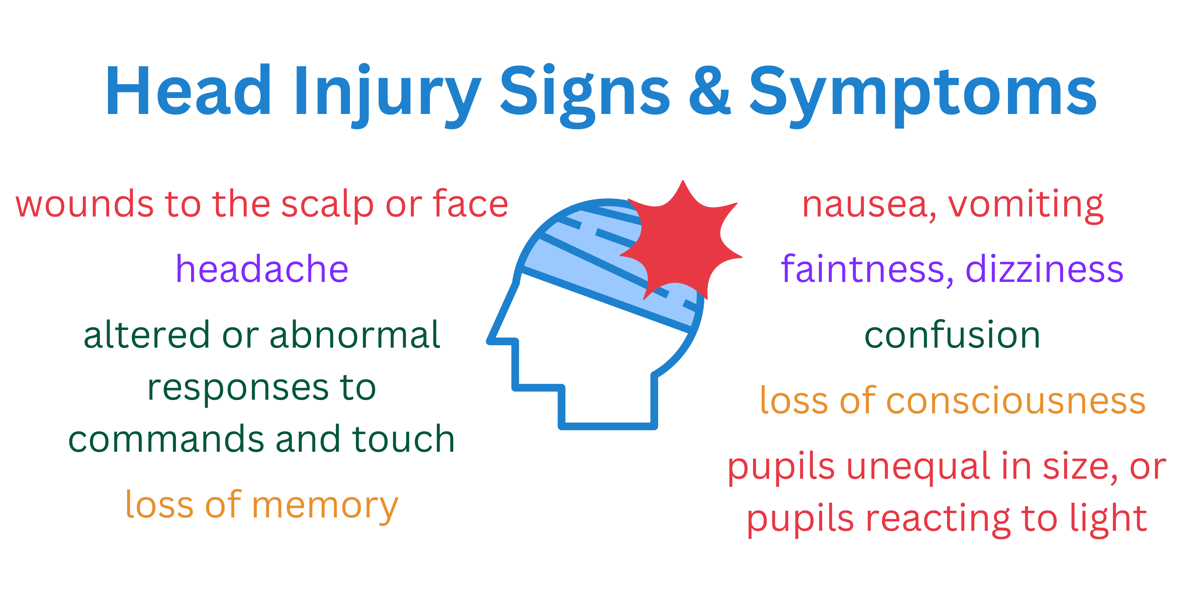
Signs and Symptoms of a Head Injury
This is especially important if you weren’t on the scene at the time, for example at a car accident. If you observe any of the following, proceed as if there is a possible head injury.
Note these head injury symptoms and signs are not always present.
Head Injury Treatment with First Aid

A casualty with a head injury may vomit, so be ready to turn them onto their side and clear the airway quickly. Support their head and neck through this process, you will need at least one helper to assist.
With little padding around the scalp to absorb knocks and bumps, the head and the brain within it are susceptible to more damage than many other parts of the body.
Even mild concussion injuries to the brain can cause long-lasting damage, especially if the casualty has experienced multiple concussions throughout their life. When undiagnosed or untreated, these can cause longer-term damage and disability. Regardless of the type of injury, even if apparently mild, medical attention is warranted and should be sought in addition to following our head injury first aid tips.


PROVIDE FIRST AID
Learn how to manage a range of common first aid scenarios.

MENTAL HEALTH AND CRISIS SUPPORT
Learn how to recognise and support people dealing with a range of common mental health issues

INFECTION CONTROL ELEARNING
Workplace infection control course completed online within 45 minutes.
